Table of Contents
Kanban Approach
Kanban is a visual project management approach emphasising continuous workflow, efficiency, and collaboration. PSL-Agile Excel Template supports the Kanban approach as a structured method for managing tasks and optimising work processes.
Kanban Concepts
Before going on the practical instructions on using PSL-Agile for the Kanban approach, it is essential to introduce its main concepts, namely briefly:
Continuous Workflow: Kanban promotes the continuous flow of work by visualising tasks and their progression through various stages. It ensures that tasks or work items move smoothly from the backlog to completion without significant bottlenecks or delays.
Backlog: The backlog represents a list of tasks or work items that must be completed. It is a repository for all upcoming work and the source for tasks pulled into the workflow.
Kanban Board: A Kanban board is a visual representation of your workflow. It is typically divided into columns representing different stages of work, such as “To-Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” Tasks move from one column to the next as they progress.
Task: A task is a specific unit of work that needs to be completed. It can represent your project's user stories, features, or any actionable item.
WIP (Work in Progress): Work in Progress refers to the number of tasks or items currently being actively worked on within a specific workflow stage, for instance, in the “In Progress” stage.
WIP Limit: To prevent overloading team members and maintain a smooth workflow, WIP limits are set for each column on the Kanban board. These limits restrict the number of tasks that can be in progress simultaneously.
Current WIP: This indicates the number of tasks in progress, helping teams stay within the WIP limits.
Lead Time: Lead time measures the total time it takes for a task to move from when it is added to the backlog to when it is completed. It includes both active work time and waiting time.
Cycle Time: Cycle time focuses solely on the active work time needed to complete a task, excluding waiting or idle time. It provides insights into how quickly tasks are completed once they enter the workflow.
By incorporating Kanban principles and utilising the Kanban board within the PSL-Agile Excel Template, you can effectively manage your project's workflow, visualise task progress, and optimise the efficiency of your team's work processes. Understanding these Kanban concepts will empower you to make informed decisions and maintain a steady and efficient project flow.
Setup Kanban Board
For implementing the Kanban approach with the PSL-Agile, you shall use the “Kanban” sheet and perform the following actions:
Define WIP: Define the Work in Progress (WIP) limit for the table “In Progress” of your Kanban board. This WIP simultaneously restricts the number of tasks in progress, ensuring a smooth workflow.
Update From ProductBacklog (Premium): Select the “Update from ProductBacklog” command (available from “PSL-Agile | Kanban”) to seamlessly copy all the in-progress product items from the product backlog to the Kanban board.
Update From SprintBacklog (Premium): Select the “Update from SprintBacklog” command (available from “PSL-Agile | Kanban”) to seamlessly copy all the in-progress task items from the sprint backlog to the Kanban board.
Manage Tasks
We delve into how to define and manage the tasks within the Kanban approach. Tasks are the core units of work that progress through different stages of the workflow.
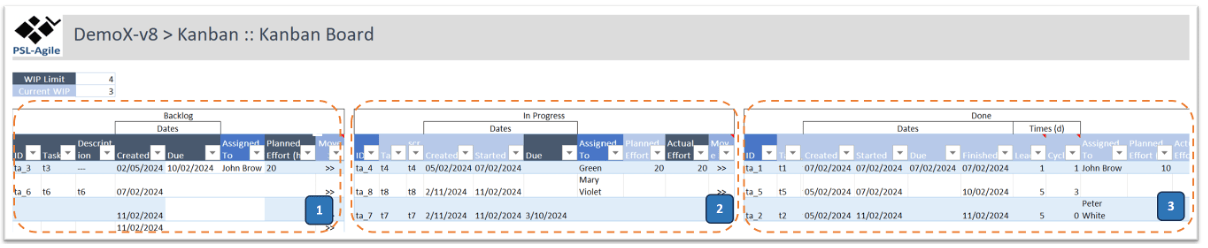
PSL-Agile provides three tables for managing these tasks according to the stages: To-Do (or Backlog), In-Progress, and Done. Generally, a task shall be added to the Backlog (To-Do) table (1). When a task is prepared to be started, it shall be moved to the In-Progress table (2); when completed, it shall be moved to the Done table (3). These tables include the following properties and actions.
Backlog (To-Do) Table
ID: The unique identifier of the task.
Task: The name of the task.
Description: Additional details or requirements related to the task.
Created Date: When the task was added to the To-Do backlog.
Due Date: When the task shall be done (if relevant to define).
Assigned to: Team member(s) assigned to this task.
Planned Effort (h): Planned effort in hours to this tasks (if relevant to define).
Actions
Double-click the “Move >” cell: Move a task from the Backlog table to the In-Progress table.
Double-click the “Description” cell: Access the user form to enter or edit the task's properties:

Double-click the “Assigned to” cell: Access a dialogue box to enter or edit the team member(s) allocation to the task. You may assign several team members with different allocation percentages:

In-Progress Table
Started Date: When the task began, i.e., was moved to the In-Progress table.
Actual Effort (h): Actual effort in hours spent with the current task.
Actions
Double-click the “Move >” cell: To move a task from the In-Progress to the Done table when the task is concluded.
Double-click the “Description” cell: Access a dialogue box to enter or edit the task's description.
Double-click the “Assigned to” cell: Access a dialogue box to enter or edit the allocation of team member(s) to the task. You may assign several team members with different allocation percentages.
Done Table
Finished Date: The date when the task was concluded, i.e., was moved to the Done table.
Lead Time: It is the period from when the task was placed on the Backboard to when it was completed (i.e., move to the Done status). Thus, this represents the total time the client waits for an item to be delivered. (Lead time = Finished date - Created date).
Cycle Time: It is the time the team spends working on this task (i.e., without the time that the task spent waiting on the Backboard). Therefore, this should start being measured when the item task enters the “In Progress” status, not earlier. (Cycle time = Finished date - Started date).
Actions
Double-click the Description cell: Access to a dialogue box to consult the task's properties and may update the task description.
Kanban Analyzer (Premium)
Based on the Kanban board (and involved tables), the Kanban Analyzer allows to monitor the progress of the work based on the Visualisation of Completed Tasks for a given period. This feature provides a table and a graphic representation of the number of completed tasks per day.
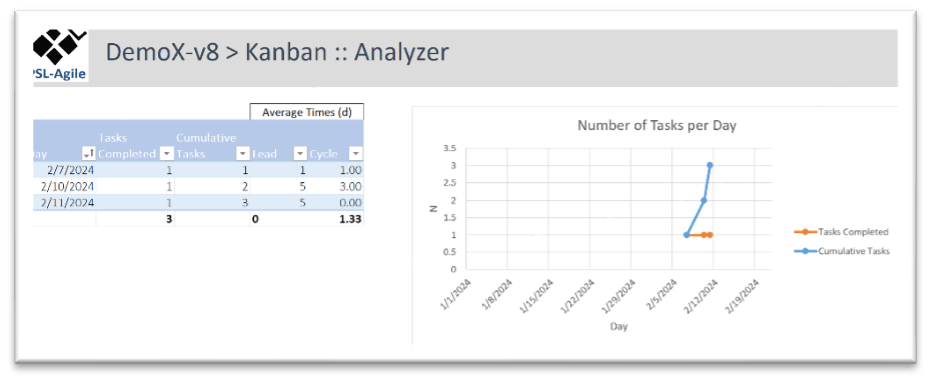
Table Structure
Day: The date of the day.
Tasks Completed: The number of tasks completed on that day.
Cumulative Tasks: The total number of tasks completed up to that day.
Lead Average Time: The average lead time for completed tasks.
Cycle Average Time: The average cycle time for completed tasks.
Actions
Graph Configuration: Customise the visual representation based on the features: Data scale, Period of dates, and graphs to show.

Update from Kanban Board: Populate the Kanban Analyzer with data from your Kanban board.
By implementing these features and practices, you can effectively manage your project using the Kanban approach, track task progress, and gain valuable insights into your team's performance through the Kanban Analyzer.
